FOR LINUX AND MAC USERS / Configuring PHP for local development (how to configure it on a production server, or if you want to tinker with nginx, see the module on vps)
For Debian-based systems
To deploy PHP projects, you need to install PHP itself. Unfortunately, Ubuntu comes with the slightly outdated PHP version 7 by default.
Therefore, in order to keep up with progress, we will connect a third-party repository that contains the latest versions of PHP. The repository is supported by Ondrej Suri, a Debian developer, so the source is reliable.
In general, we write
sudo apt install software-properties-common
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
The first command installs a package that simplifies connecting third-party repositories, and the second actually connects the repository.
Press Enter when prompted.

Once the repository has been added and the cache has been updated, you can install PHP. Type the following (you can use a different version instead of 8.2)
sudo apt install php8.2-fpm -y
And wait for it to install.
php-fpm is not just a php compiler/interpreter, it is a whole service that can be connected to nginx and will automatically execute scripts and return the results of their processing back to the user.
For Macs
I haven’t tested it, but in theory, it should be enough to execute the command
brew install php
Here’s another useful link
Setting up the development process
In principle, you can deploy everything as for VPS, but for now, it is enough to configure PHP for local development. Check that PHP is installed correctly:
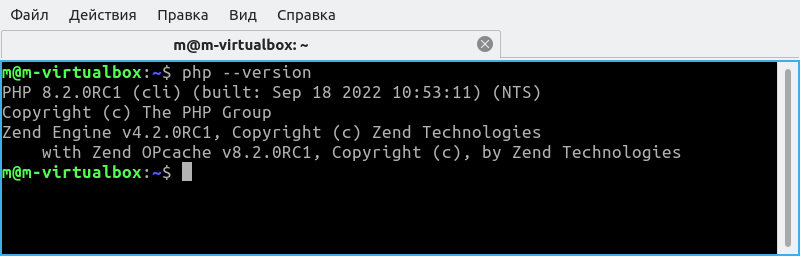
Install the PHP plugin in Visual Studio Code
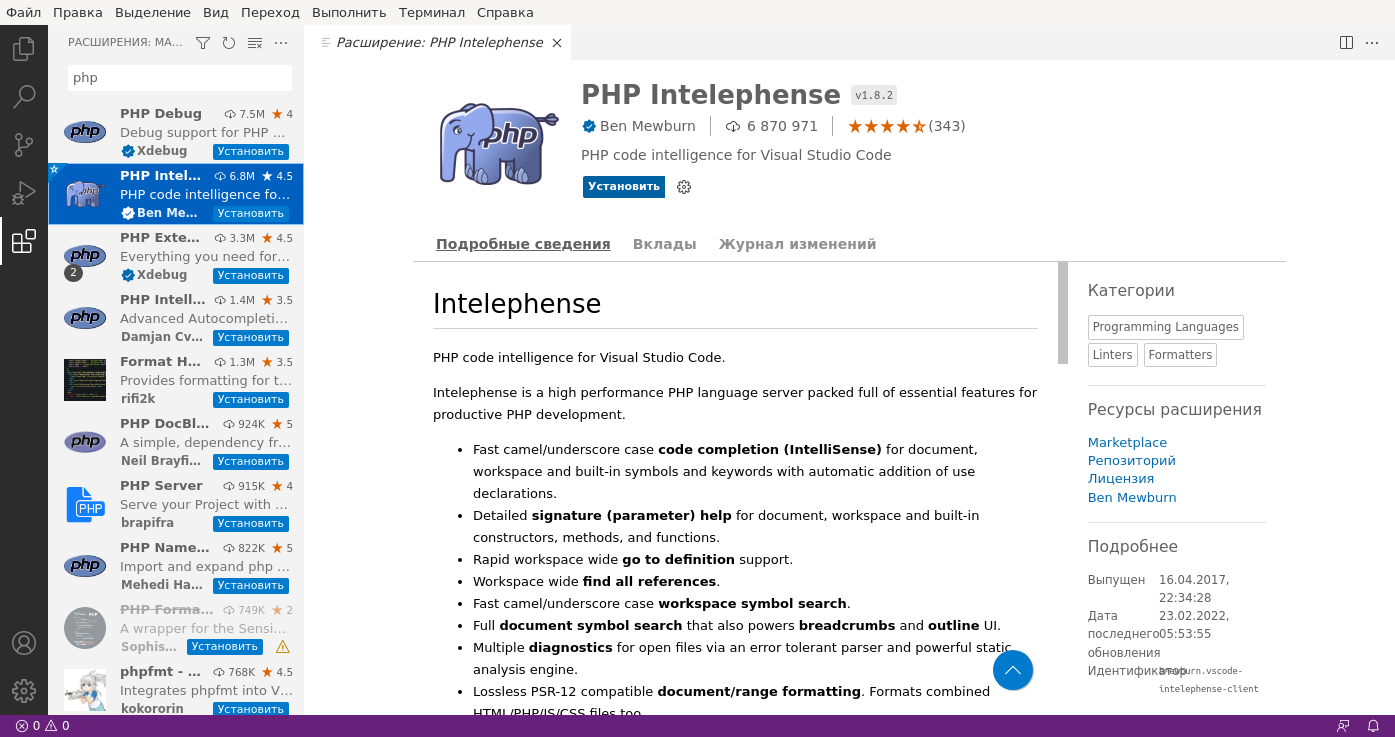
Now you can create a folder with the project and create a file called index.php
in it.
<?php echo phpinfo(); ?>
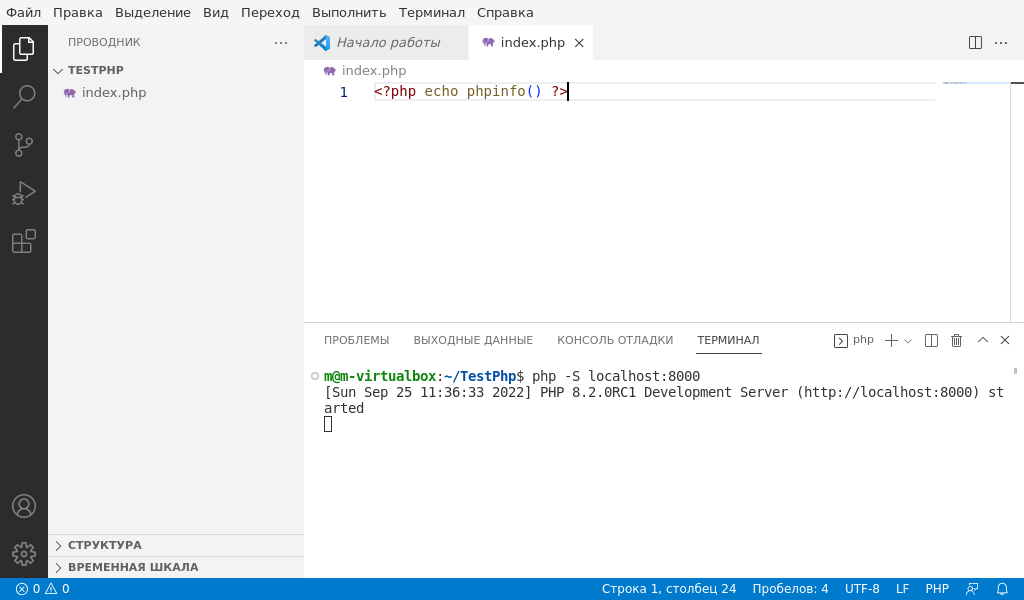
Open the terminal and type
php -S localhost:3000
Like this
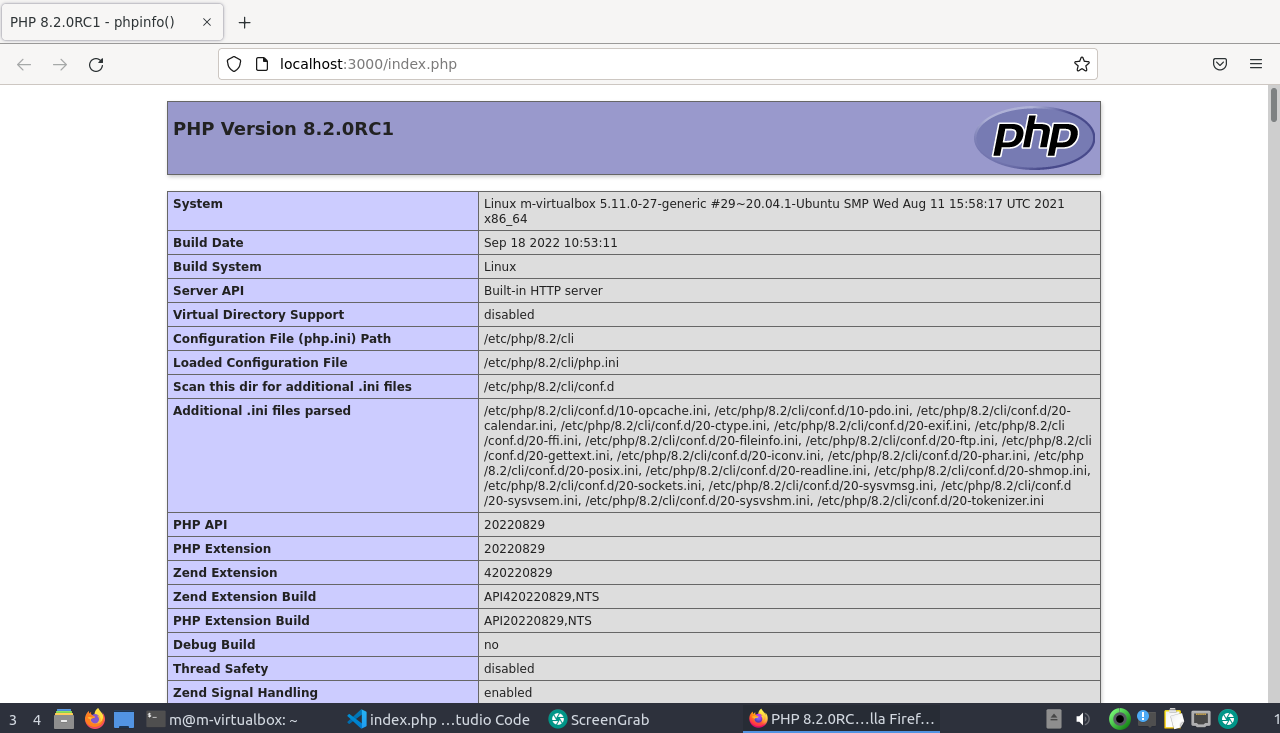
Now open http://localhost:3000 in your browser
And there you go:
You can start developing =)